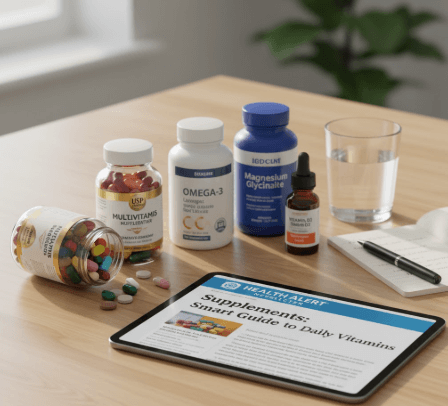
Core Vitamins That Cover the Basics
For most healthy adults, a balanced multivitamin fills in occasional nutritional gaps. Vitamin D3 is crucial for bone, immune, and mood support—especially if you live in northern climates or spend little time in the sun. Magnesium glycinate is gentle on the gut, supports sleep, and helps manage stress. Omega-3s (from fish oil or algae) benefit both heart and brain function, and are often lacking in Western diets.
- Teenagers & Young Adults: Focus on calcium and vitamin D during growth spurts; consider an iron supplement if your doctor recommends it.
- Adults 40+: B vitamins (especially B12), vitamin D3, and magnesium become more important as absorption and needs shift with age.
- Pregnant or Breastfeeding: Choose prenatal vitamins with methylfolate (rather than folic acid) and check for appropriate iron, iodine, and DHA levels.
How to Read Supplement Labels
- Look for third-party testing seals such as USP, NSF, or Informed-Choice to ensure product quality and ingredient accuracy.
- Compare the “% Daily Value” to ensure you aren’t megadosing. Getting more than 100% of the daily value of some vitamins, like A or E, can be harmful.
- Avoid fillers like artificial colors, titanium dioxide, and hydrogenated oils. Watch for unwanted binders, sweeteners, and flavorings.
- For herbals or adaptogens, check standardized extract percentages for potency—look for clinical research supporting their use.
Pro Tip
Pair fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K) with a meal that contains healthy fats for better absorption. For example, take vitamin D with breakfast containing avocado or eggs.
Common Supplement Pitfalls
- Mixing interactions: Calcium can block iron absorption; magnesium may interfere with some antibiotics. Space out doses when needed.
- Going overboard: More is not always better. Excessive intake can strain kidneys or liver.
- One-size-fits-all: Individual needs differ. Genetics, lifestyle, health conditions, and medications all change what’s best for you.
- "All Natural" ≠ Safer: Herbal supplements can still interact with medications or trigger side effects—verify with your provider.
When to Talk to Your Doctor
Review your supplement list during annual checkups, especially if you take prescriptions. Blood work can reveal real nutrient gaps and prevent overlaps or risky combinations. Bring your pill bottles or take pictures of labels to appointments for an easy review.
Consider extra testing if you follow a restricted diet (vegan, gluten-free), have a chronic health condition, or have had bariatric surgery—these situations may benefit from customized supplement strategies.
“Clarity beats quantity. A targeted regimen based on lab work is a smarter investment than a shelf full of random pills,” says Dr. Elise Navarro.
Simple Daily Routine Example
A sample daily supplement trio for a healthy adult:
- 1 high-quality multivitamin with breakfast
- Vitamin D3 (1000-2000 IU) during winter months or as recommended
- Omega-3 capsule with lunch or dinner (ideally with a meal containing fat)
- Magnesium glycinate at night to support restful sleep